
 What is a geomagnetic storm?
What is a geomagnetic storm?
A Geomagnetic Storm is a disturbance in the Earth's magnetic field, that may disrupt HF communication and trigger auroras↗.
What are the impacts of a geomagnetic storm?
A major magnetic storm can disrupt HF propagation by changing the distribution of free electrons in the ionosphere. It has three phases: initial, main, and recovery.
What causes geomagnetic storms? — Solar flares and coronal mass ejections:
- Solar X-Ray radiation bursts known as solar flares:
- Solar wind containing charged particles colide with Earth's Magnetosphere.
Significant events are named "Coronal Mass Ejections" (CMEs):
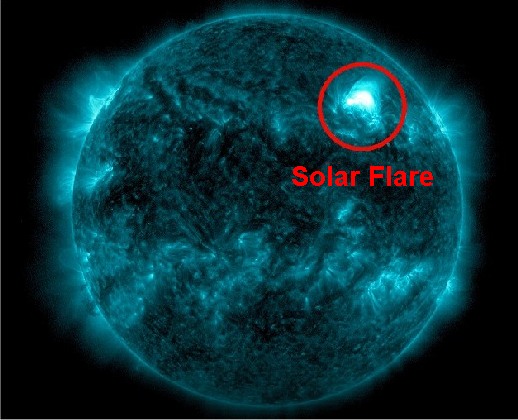

A Solar Flare courtesy of NOAA, May 2023
A CME↗ is a shock-wave of Solar Energetic Particles ↗ emitted by the sun.
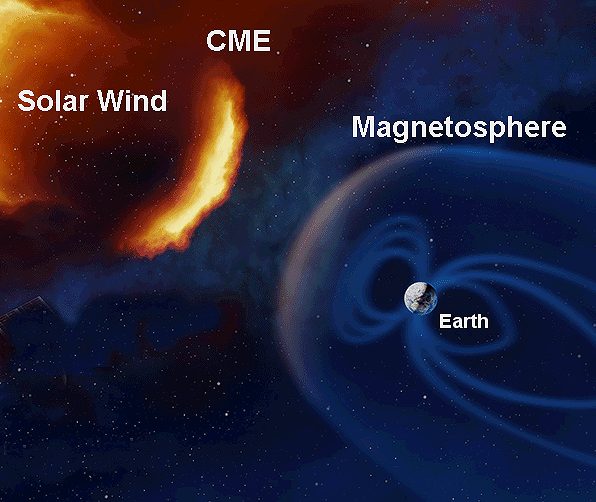
When a CME enters the magnetosphere, it causes a Geomagnetic Storm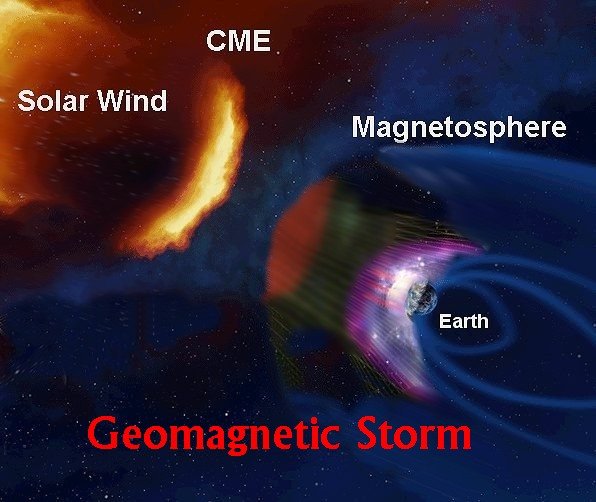
How are geomagnetic storms defined?
A geomagnetic storm is defined by changes in the "Disturbance-storm time" (Dst) index. The Dst index estimates the globally averaged change of the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field at the magnetic equator based on measurements from a few magnetometer stations. Dst is computed once per hour and reported in near-real-time.
How are geomagnetic storms classified?
At quiet time (no storm) ranges from +20 to −20 nano-Tesla (nT). The magnitudes of storms are classified as moderate (from 50 nT to 100 nT), intense (from 100 nT to 250 nT), or super-storm (above 250 nT).
How are geomagnetic storms quantified?
The Kp index quantifies the geomagnetic disturbances, "correlating with G-scale".
- References:
- May 2024 Solar Storms Wikipedia
- Geomagnetic Storms May 2024 Duckduckgo
shows near-real-time indices and explains what the terms mean.