 Radio Communication Circuit
Radio Communication Circuit
Introduction to Wireless Communications: Radio Frequency Transmission and Reception
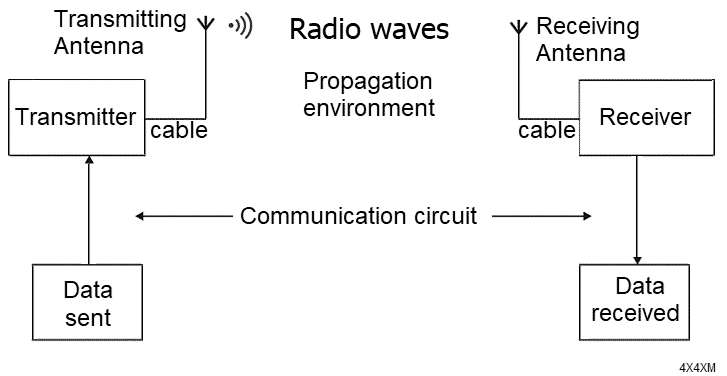
Figure 1 illustrates the transmission of radio frequencies (RF) as electromagnetic waves for long-distance communication. A transmitter generates currents in an antenna, converting them into radio waves that propagate away. Receiving antennas capture these waves and transform them into electrical signals, which reproduce audio, video, or other data.
This process allows for the seamless transmission of information over vast distances, making radio technology essential for various forms of communication, including broadcasting and wireless networking. The conversion of radio waves back into electrical signals is crucial for delivering content to end users.
The project "Understanding HF Propagation" focuses on skywave propagation via the ionosphere.
HF propagation status and alerts
Real time radio propagation map
HF propagation for hams explained
Current solar conditions Ham radio
Current Ham Radio HF Propagation
HF Radio Propagation Search Terms
Concept of wireless communication
The Path of Wireless Communication
Telecommunication circuit illustration
Radio propagation for hams explained
Plan HF communication on ham bands
Current HF Band Conditions Online Map
Introduction to Wireless Communications
Current Ham Radio Propagation Conditions
Real-time watching of worldwide ham activity
How does the sun affect radio communication?
Real-time watching of worldwide activity of hams
The Fascinating World of HF Skywave Propagation
Current HF Bands Conditions—Charts for Radio Hams
Current HF Band Conditions Maps For Radio Operators
The Path of Wireless Communication
Introduction to Wireless Communications
24-hour forecast for point-to-point communication circuit